Encryption vs. Secure Erasure: A Comprehensive Guide

Intoduction
In an age where data breaches and cyber threats are increasingly common, ensuring the security of sensitive information has become a top priority for businesses and individuals. Two primary methods for safeguarding data are encryption and secure erasure. Although both serve the purpose of protecting data, they address different aspects of data security. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the ins and outs of encryption and secure erasure to help you determine the best approach for your data protection needs.
Understanding Encryption
Encryption is a process that involves using mathematical algorithms and encryption keys to convert plaintext data into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable to anyone without the correct decryption key. This process ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to encrypted data, they won't be able to decipher its contents.
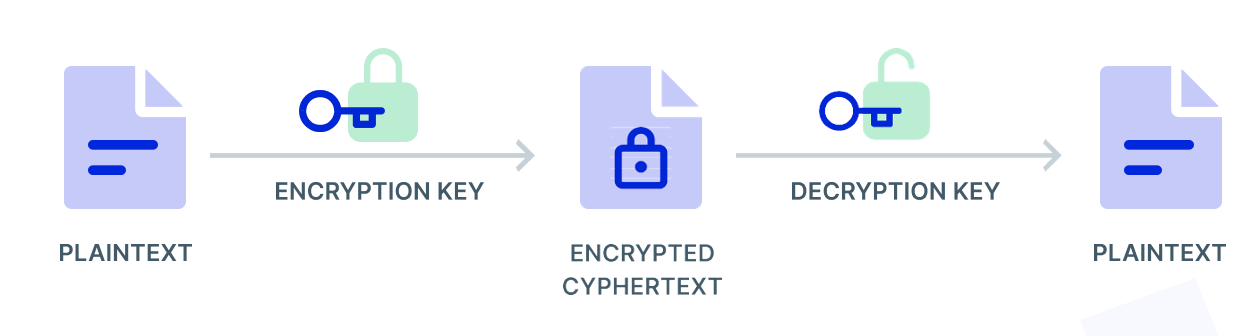
-
Types of Encryption: There are two primary types of encryption – symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses different keys for each process. Both types have their advantages and use cases, with symmetric encryption typically being faster, and asymmetric encryption offering better security.
-
Encryption Algorithms: Various encryption algorithms are available to provide different levels of security. Some common examples include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), and Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (Triple DES). Choosing the right algorithm depends on factors such as the type of data, the required level of security, and the desired performance.
-
Key Management: Proper key management is crucial for maintaining encryption security. This includes generating strong keys, securely storing them, and implementing regular key rotation. Failure to manage keys effectively can lead to unauthorized access to encrypted data.
Secure Erasure Explained
Secure erasure is the process of permanently and irreversibly removing data from a storage device. This ensures that the data cannot be recovered by any means, even with advanced data recovery tools. Secure erasure is particularly important when disposing of or repurposing storage devices to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.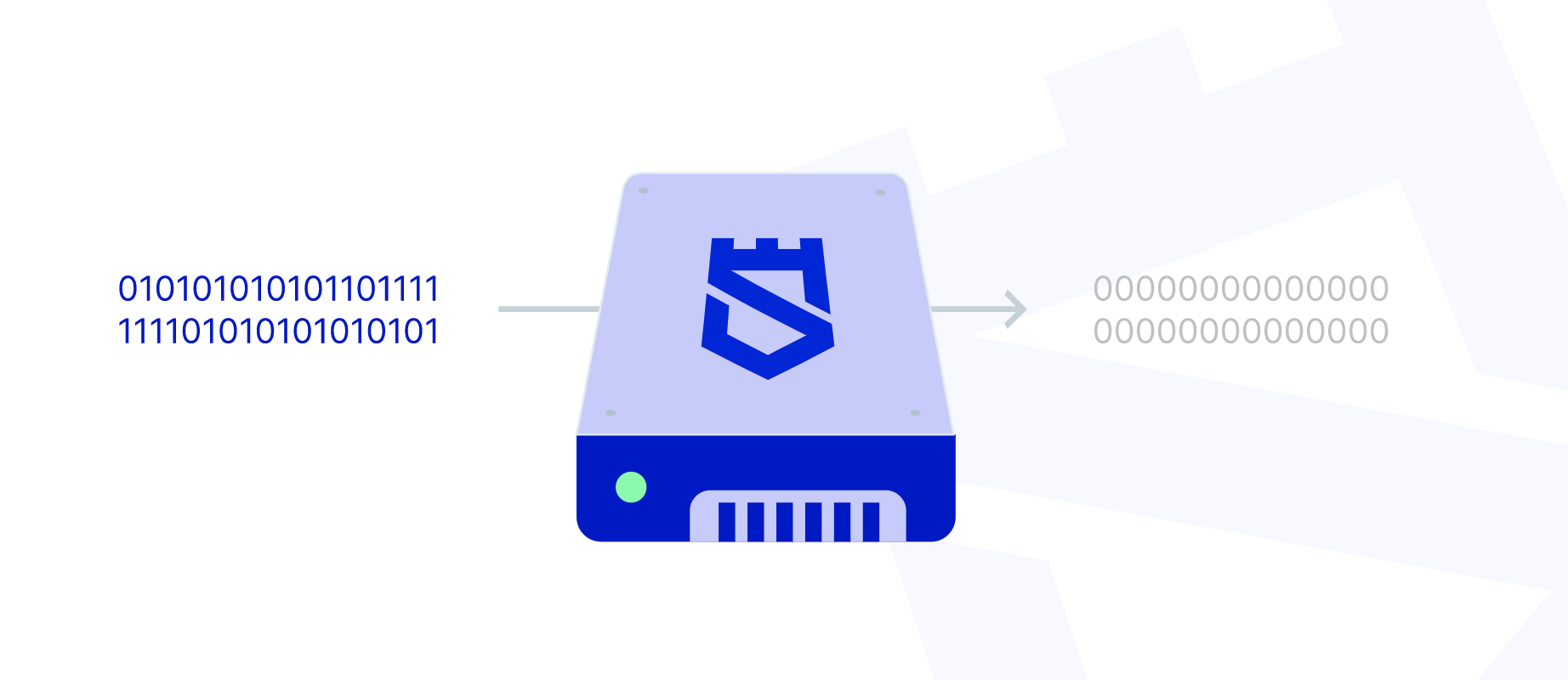
-
Data Sanitization Methods: Various methods can be used to perform secure erasure, including overwriting, degaussing, and physical destruction. Overwriting replaces existing data with random patterns, degaussing uses strong magnetic fields to erase data, and physical destruction involves completely destroying the storage medium.
-
Standards and Certifications: Several standards and certifications govern secure data erasure, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guidelines, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) standards, and industry-specific regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). In addition to these standards, our own SEC-2021-SSD Performance (NIST 800-88 compliant) standard, which is Common Criteria certified, ensures a high level of security and compliance for data erasure.
-
Erasure Verification: To ensure that data has been securely erased, it's essential to verify the erasure process. This can be achieved through techniques like audit trails, certificates of erasure, and third-party verification.
Why You Need Both Encryption and Secure Erasure
While encryption provides protection against unauthorized access during a data's active lifecycle, secure erasure ensures that sensitive information is permanently removed at the end of its lifecycle. Combining both methods ensures a comprehensive approach to data security.
-
Layered Security: Implementing both encryption and secure erasure creates a layered security approach, providing protection during data storage, transmission, and disposal.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards often requires both encryption and secure erasure to ensure full compliance.
-
Risk Mitigation: Combining encryption and secure erasure helps mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and improper disposal of storage devices.
To help you visualize this comprehensive approach, refer to the graphic included below. It represents the data lifecycle, starting with firewall and antivirus protection, followed by patch management to keep systems up-to-date. Next, encryption is applied to secure data during its active lifecycle. Finally, Securaze's secure erasure solutions ensure the permanent and irreversible removal of sensitive data at the end of the lifecycle, effectively closing the loop on data protection.
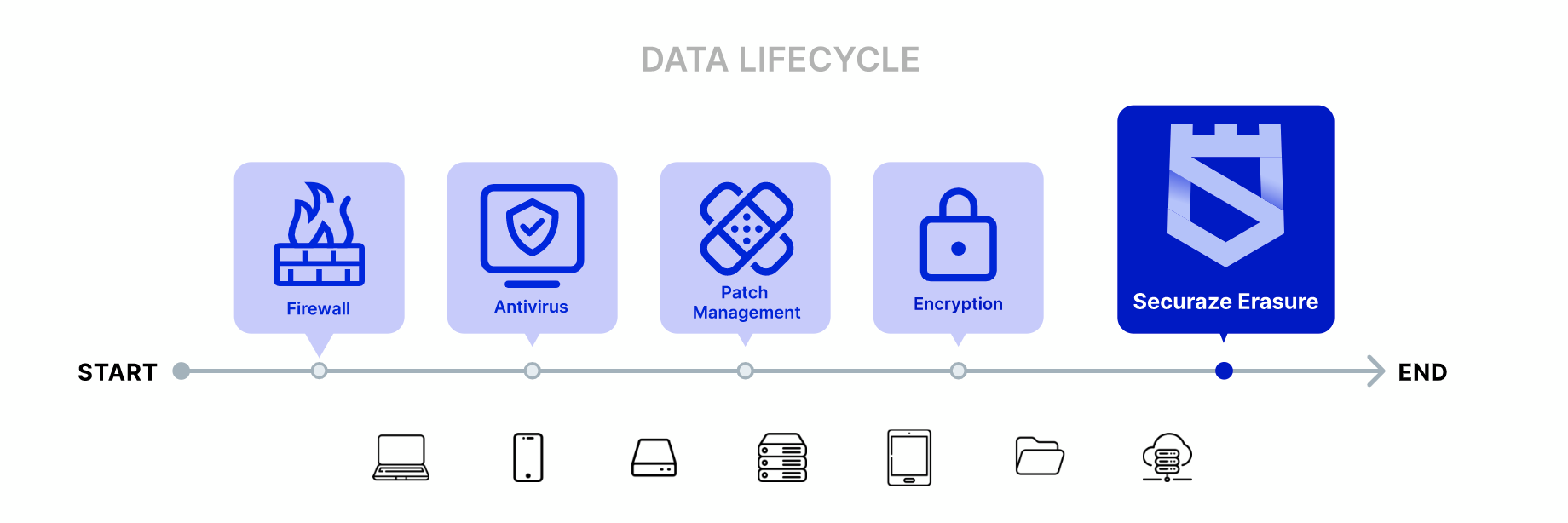
Conclusion
In conclusion, both encryption and secure erasure play critical roles in ensuring data security throughout the entire data lifecycle. By understanding and implementing these methods, businesses and individuals can better protect their sensitive information during storage, transmission, and disposal. A comprehensive approach to data security requires combining encryption and secure erasure to mitigate risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and improper disposal of storage devices.
To achieve the highest standards in secure data erasure, turn to Securaze for reliable and compliant solutions. Our industry-leading methods adhere to stringent standards and certifications, including our own SEC-2021-SSD Performance (NIST 800-88 compliant) standard, which is Common Criteria certified. Trust Securaze to help protect your sensitive data and maintain regulatory compliance throughout the data lifecycle.
For more information please visit our website or contact us at: www.securaze.com

.png)